Integrating Gravity Forms with Next.js
This guide demonstrates the implementation of a headless contact form using Next.js and WordPress Gravity Forms. You’ll learn how to create a form, handle submissions, and implement validation while maintaining a seamless user experience.
Alternative free implementation: Integrating Contact Form 7 with Next.js
Requirements
- WordPress installation with Gravity Forms plugin
- Next.js 15 application with App Router
Implementation
WordPress Configuration
Gravity Forms Setup
-
Create a new form in Gravity Forms with the following fields. These field IDs are crucial as they’ll be used in our Next.js implementation:
- First Name
- Last Name
- Message
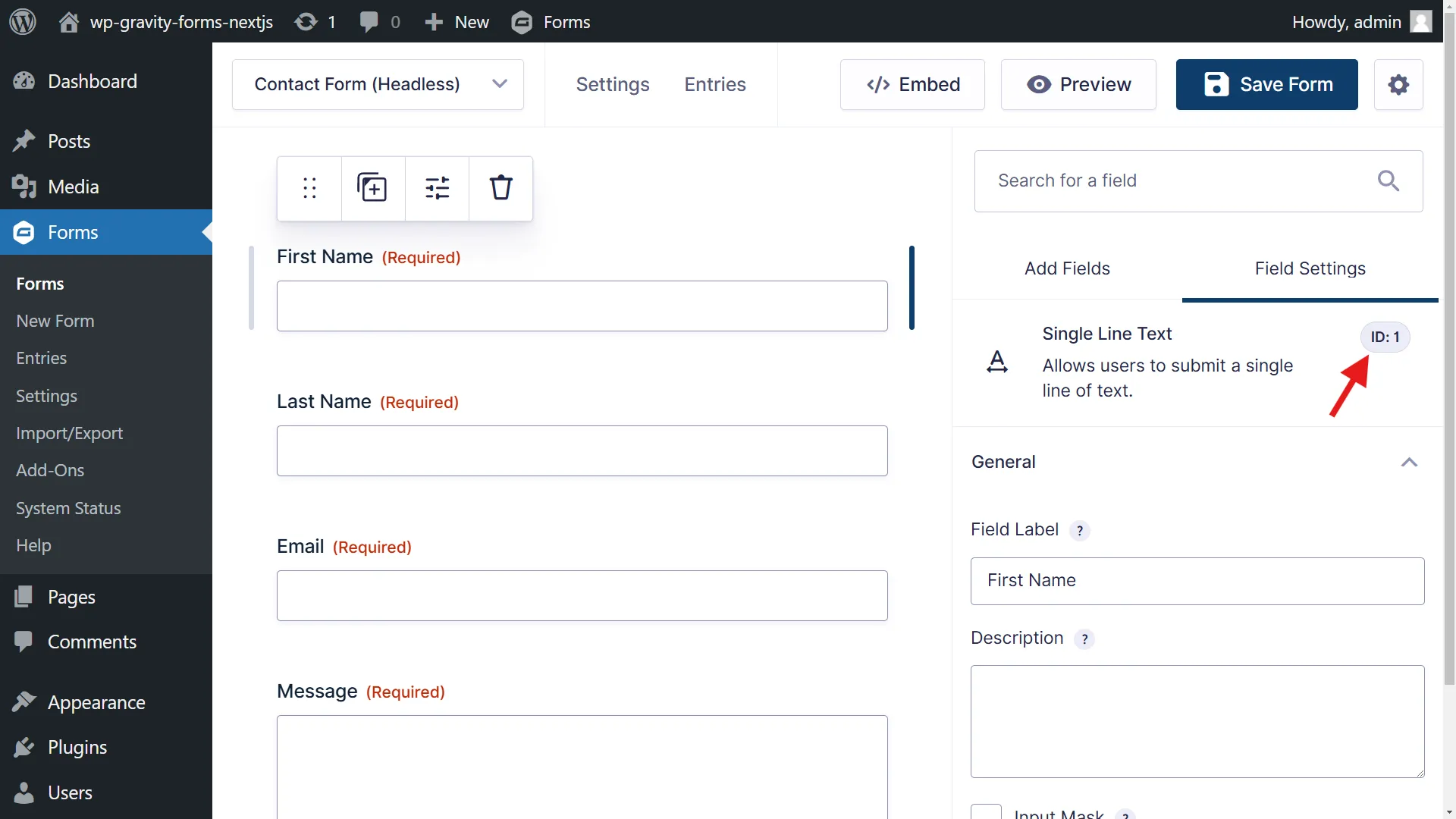
-
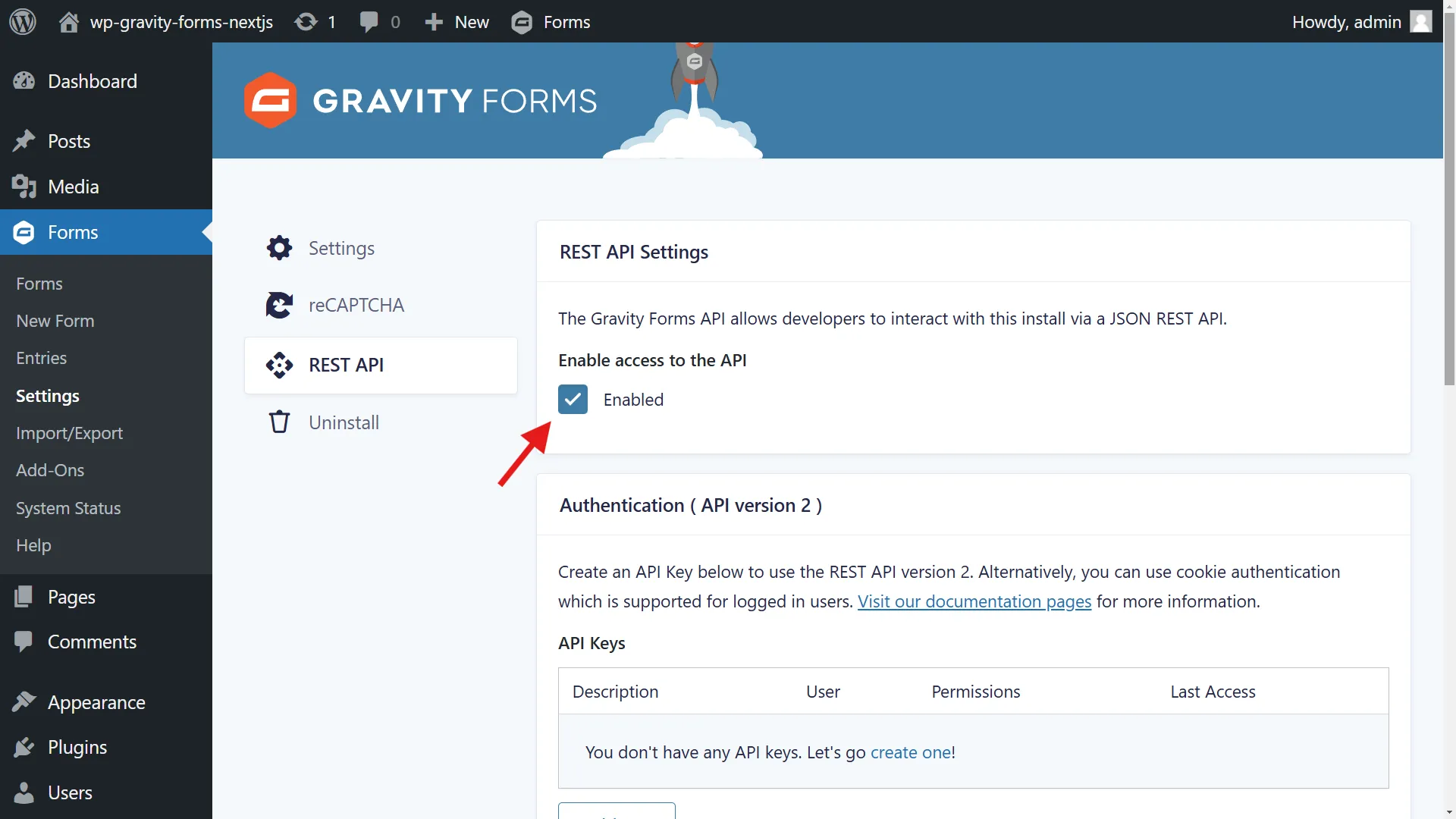
Enable REST API access. This is required for our Next.js application to communicate with Gravity Forms:
- Navigate to WordPress Admin > Forms > Settings
- Select “REST API” tab
- Enable “Enable access to the API”
Next.js Implementation
1. UI Components Setup (Optional)
We’ll use shadcn/ui for a polished, accessible form interface. Install it with:
npx shadcn@latest initAdd the required components that we’ll use in our form:
npx shadcn@latest add button input textarea label2. Form Component
Create the base form structure. Note that the input names must match exactly with the field IDs from Gravity Forms:
import { Button } from "./ui/button"import { Input } from "./ui/input"import { Label } from "./ui/label"import { Textarea } from "./ui/textarea"
export function ContactForm() { return ( <form className="w-full max-w-3xl rounded-lg bg-white px-4 py-12"> <div className="mx-auto max-w-2xl space-y-6"> <h1 className="text-center text-4xl">Contact</h1> <div className="flex gap-4"> <div className="flex-1 space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_1">First Name</Label> <Input id="input_1" name="input_1" /> </div> <div className="flex-1 space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_3">Last Name</Label> <Input id="input_3" name="input_3" /> </div> </div> <div className="space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_4">Email</Label> <Input id="input_4" name="input_4" /> </div> <div className="space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_5">Message</Label> <Textarea id="input_5" name="input_5" /> </div> <Button type="submit">Send</Button> </div> </form> )}Add to homepage:
import { ContactForm } from "@/components/contact-form"
export default function HomePage() { return ( <main className="flex min-h-screen items-center justify-center bg-slate-200"> <ContactForm /> </main> )}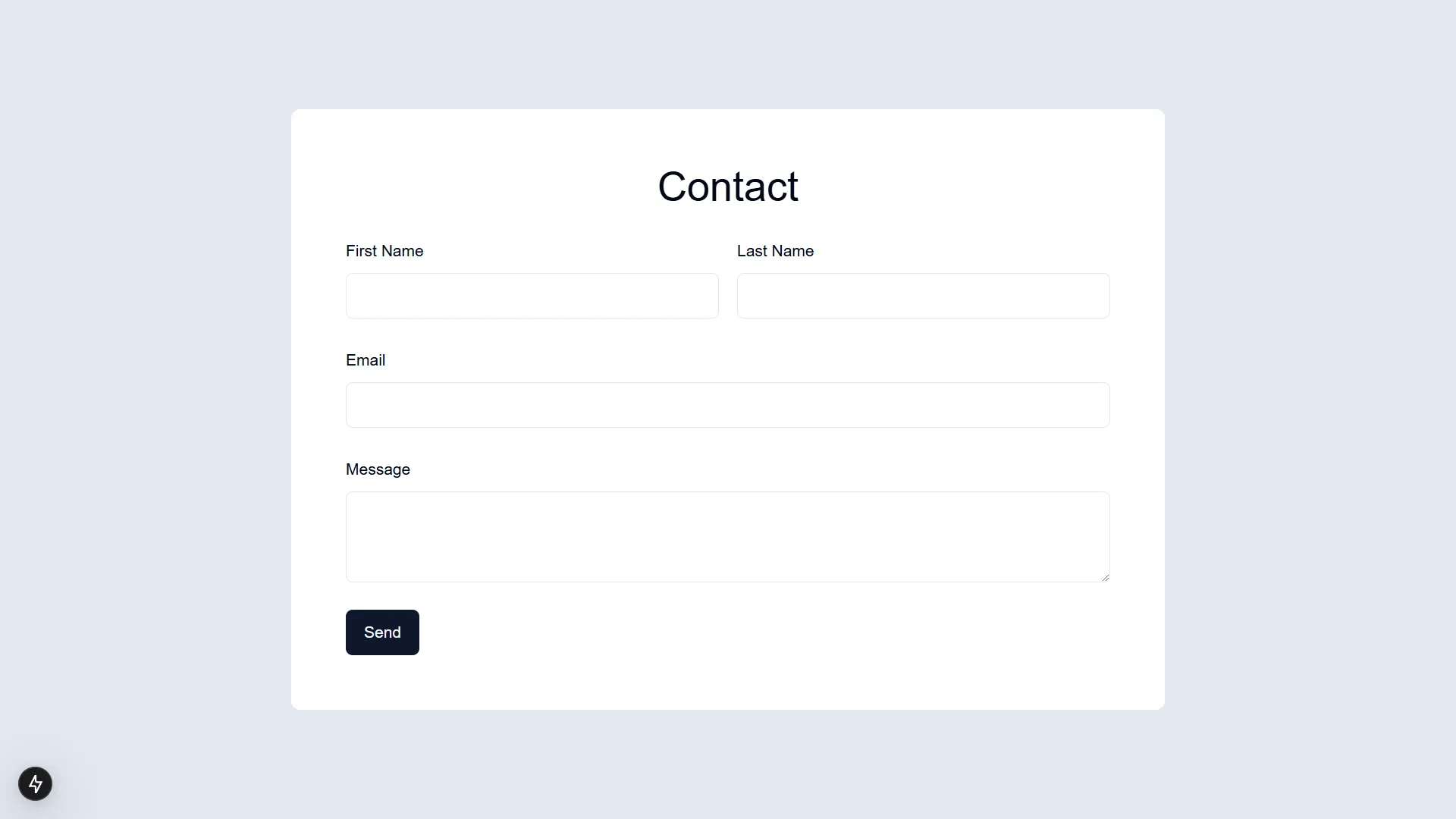
3. Form Submission Handler
Before implementing form submission, you’ll need the form ID from your Gravity Forms setup. You can find this in the WordPress admin panel under Forms:
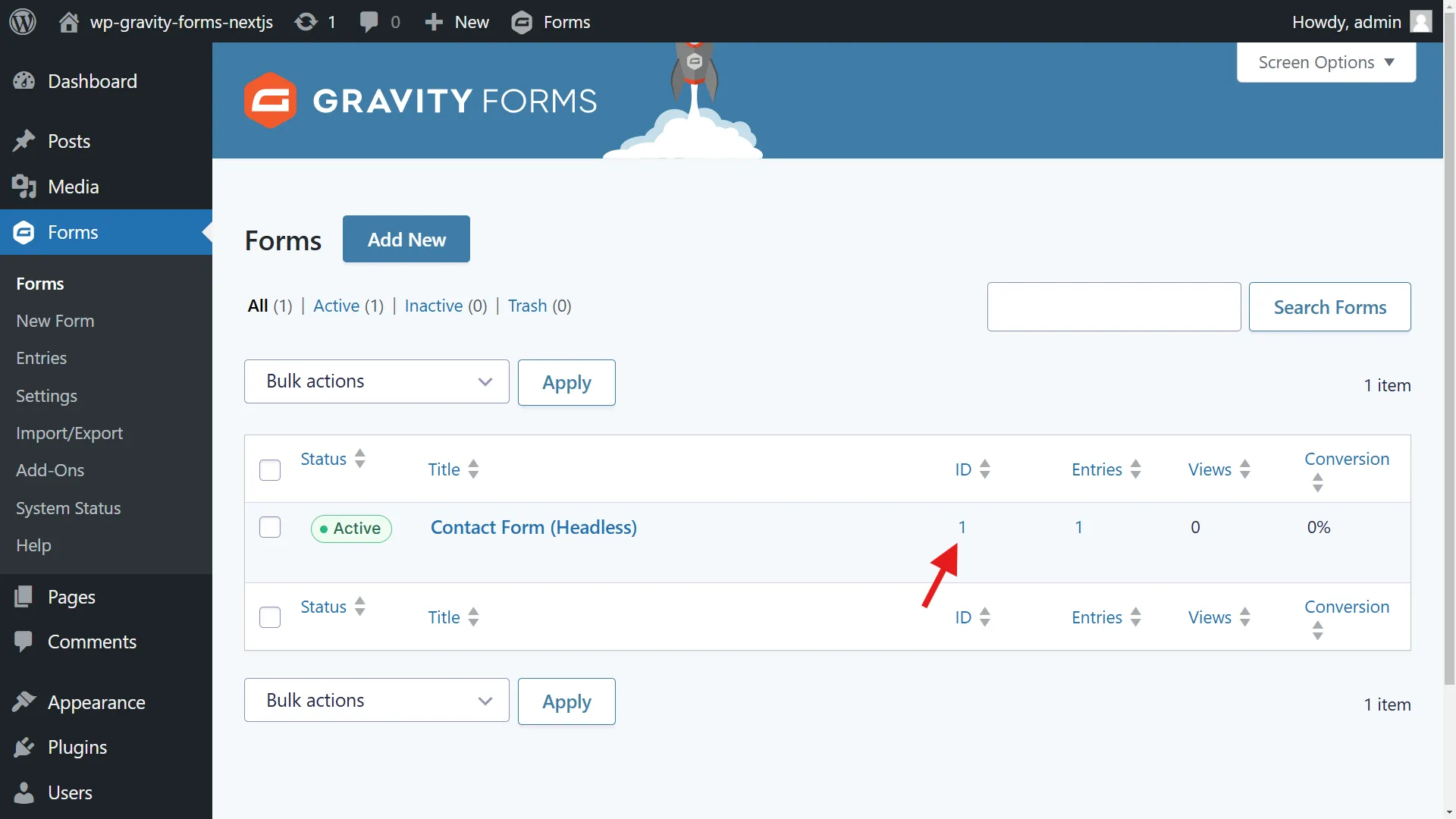
Create a server action to handle form submissions:
"use server"
export async function sendFormData(formData: FormData) { try { const response = await fetch( // Replace with your site URL and Form ID "http://yt-gf-nextjs.local/wp-json/gf/v2/forms/1/submissions", { method: "POST", body: formData, }, )
const data = await response.json()
return data } catch (error) { console.error("Error submitting form:", error) return { error: "An unexpected error has occurred. Please try again later.", } }}4. Form Validation
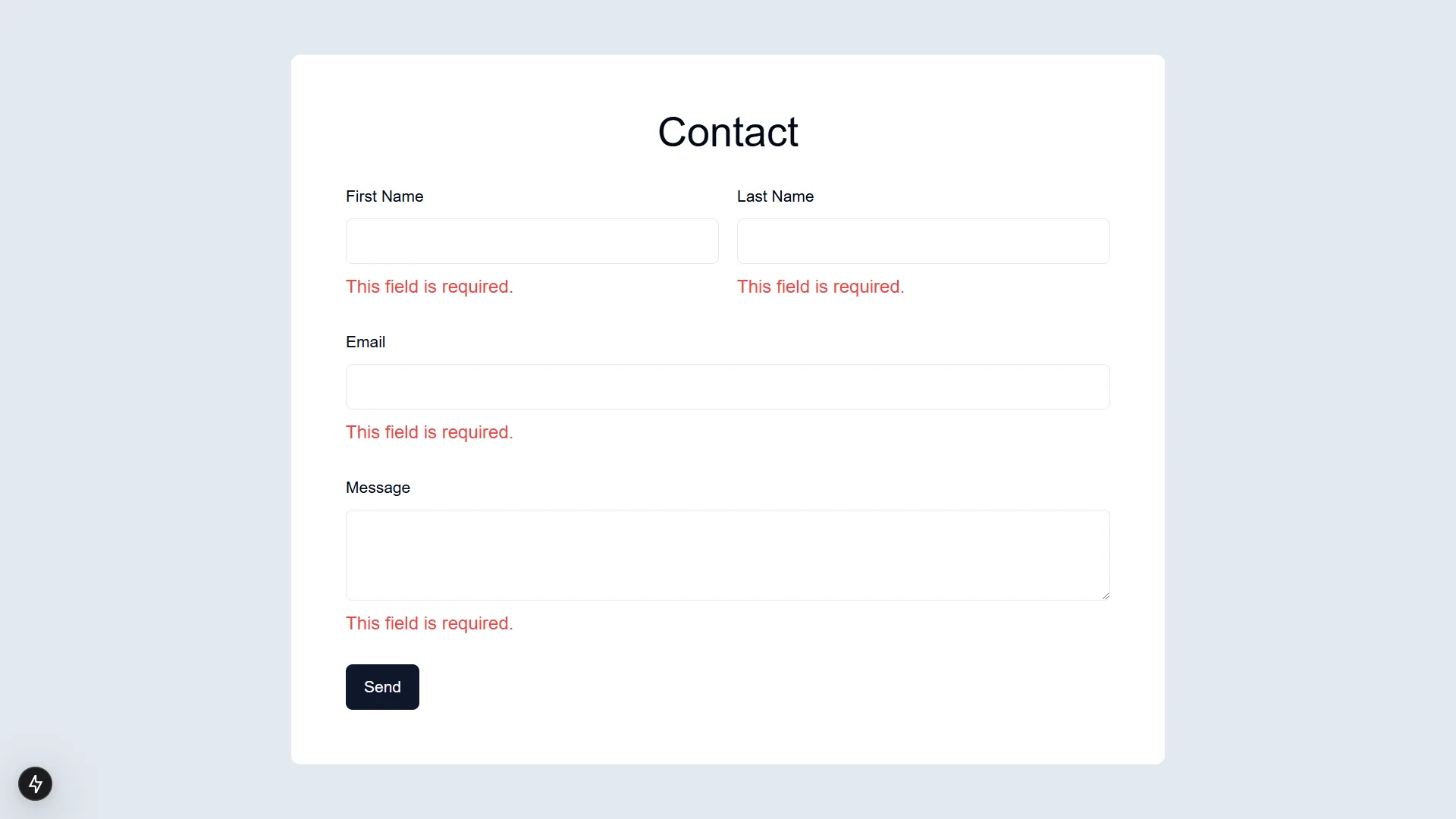
Gravity Forms provides validation feedback through its API response. Here’s an example of the response structure when validation fails:
{ "is_valid": false, "validation_messages": { "3": "This field is required.", "4": "The email address entered is invalid, please check the formatting (e.g. email@domain.com)." }}The form component is marked as a client component to handle client-side state and interactions. It uses the useActionState hook to manage form submission state and displays validation messages:
"use client"
import { useActionState } from "react"import { Button } from "./ui/button"import { Input } from "./ui/input"import { Label } from "./ui/label"import { Textarea } from "./ui/textarea"import { sendFormData } from "@/server/actions"
export function ContactForm() { const [state, action, isPending] = useActionState(sendFormData, {})
return ( <form action={action} className="w-full max-w-3xl rounded-lg bg-white px-4 py-12" > <div className="mx-auto max-w-2xl space-y-6"> <h1 className="text-center text-4xl">Contact</h1> <div className="flex gap-4"> <div className="flex-1 space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_1">First Name</Label> <Input id="input_1" name="input_1" /> {state.validation_messages?.["1"] && ( <p className="text-destructive"> {state.validation_messages["1"]} </p> )} </div> <div className="flex-1 space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_3">Last Name</Label> <Input id="input_3" name="input_3" /> {state.validation_messages?.["3"] && ( <p className="text-destructive"> {state.validation_messages["3"]} </p> )} </div> </div> <div className="space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_4">Email</Label> <Input id="input_4" name="input_4" /> {state.validation_messages?.["4"] && ( <p className="text-destructive">{state.validation_messages["4"]}</p> )} </div> <div className="space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_5">Message</Label> <Textarea id="input_5" name="input_5" /> {state.validation_messages?.["5"] && ( <p className="text-destructive">{state.validation_messages["5"]}</p> )} </div> <Button type="submit">Send</Button> <Button type="submit" disabled={isPending}> {isPending ? "Sending..." : "Send"} </Button> {state.is_valid && <p>{state.form.confirmation.message}</p>} {state.error && <p className="text-destructive">{state.error}</p>} </div> </form> )}The function passed to useActionState receives an extra argument, the previous or initial state, as its first argument:
"use server"
export async function sendFormData(prevState: unknown, formData: FormData) { try { const response = await fetch( // Replace with your site URL and Form ID "http://yt-gf-nextjs.local/wp-json/gf/v2/forms/1/submissions", { method: "POST", body: formData, }, )
const data = await response.json()
return data } catch (error) { console.error("Error submitting form:", error) return { error: "An unexpected error has occurred. Please try again later.", } }}The validation messages are displayed with a destructive (error) styling and appear only when validation fails for that specific field. The form uses the isPending state from useActionState to disable the submit button and show a loading state during submission. Success and error messages are displayed at the bottom of the form based on the submission state.
5. Preserving Form Input Values After Validation Errors
When form validation fails, we want to preserve the user’s input to avoid data loss. The server action returns the form data in the response, which we use to populate the form fields:
"use server"
export async function sendFormData(prevState: unknown, formData: FormData) { try { const response = await fetch( // Replace with your site URL and Form ID "http://yt-gf-nextjs.local/wp-json/gf/v2/forms/1/submissions", { method: "POST", body: formData, }, )
const data = await response.json()
if (!data.is_valid) { data.payload = formData }
return data } catch (error) { console.error("Error submitting form:", error) return { error: "An unexpected error has occurred. Please try again later.", payload: formData, } }}The form component uses this returned data to set the default values of input fields:
"use client"
import { useActionState } from "react"import { Button } from "./ui/button"import { Input } from "./ui/input"import { Label } from "./ui/label"import { Textarea } from "./ui/textarea"import { sendFormData } from "@/server/actions"
export function ContactForm() { const [state, action, isPending] = useActionState(sendFormData, {})
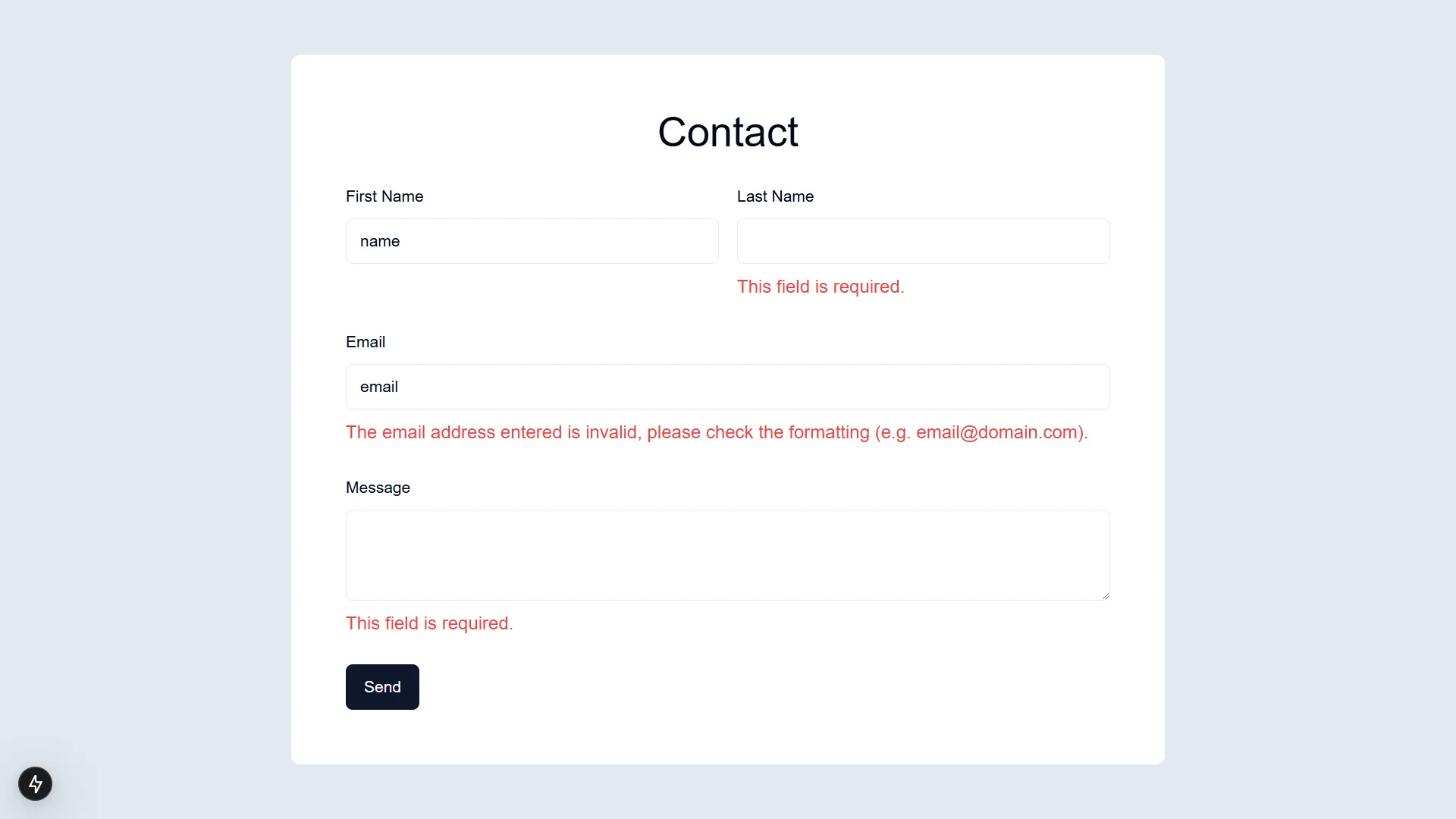
return ( <form action={action} className="w-full max-w-3xl rounded-lg bg-white px-4 py-12" > <div className="mx-auto max-w-2xl space-y-6"> <h1 className="text-center text-4xl">Contact</h1> <div className="flex gap-4"> <div className="flex-1 space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_1">First Name</Label> <Input id="input_1" name="input_1" defaultValue={state.payload?.get("input_1") || ""} /> {state.validation_messages?.["1"] && ( <p className="text-destructive"> {state.validation_messages["1"]} </p> )} </div> <div className="flex-1 space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_3">Last Name</Label> <Input id="input_3" name="input_3" defaultValue={state.payload?.get("input_3") || ""} /> {state.validation_messages?.["3"] && ( <p className="text-destructive"> {state.validation_messages["3"]} </p> )} </div> </div> <div className="space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_4">Email</Label> <Input id="input_4" name="input_4" defaultValue={state.payload?.get("input_4") || ""} /> {state.validation_messages?.["4"] && ( <p className="text-destructive">{state.validation_messages["4"]}</p> )} </div> <div className="space-y-2"> <Label htmlFor="input_5">Message</Label> <Textarea id="input_5" name="input_5" defaultValue={state.payload?.get("input_5") || ""} /> {state.validation_messages?.["5"] && ( <p className="text-destructive">{state.validation_messages["5"]}</p> )} </div> <Button type="submit" disabled={isPending}> {isPending ? "Sending..." : "Send"} </Button> {state.is_valid && <p>{state.form.confirmation.message}</p>} {state.error && <p className="text-destructive">{state.error}</p>} </div> </form> )}This ensures that users don’t have to re-enter their data when validation errors occur.
Conclusion
This implementation provides a complete solution for integrating Gravity Forms with Next.js, including:
- Server-side form submission using Next.js Server Actions
- Client-side validation with Gravity Forms API
- Form state preservation on validation errors
- Error handling and user feedback
- Responsive UI components using shadcn/ui